Reductive amination of carbonyls to primary amines is of importance to the synthesis of fine chemicals; however, this reaction with heterogeneous catalysts containing earth-abundant metals under mild conditions remains scarce. Here, we show that the nickel catalyst with mixed oxidation states enables such synthesis of primary amines under low temperature (50 °C) and H2 pressure (0.9 MPa). The catalyst shows activity in both water and toluene. The high activity likely results from the formation of small (ca. 4.6 nm) partially oxidized nickel nanoparticles (NPs) homogeneously anchored onto the silica and their synergistic effect. Detailed characterizations indicate stabilization of NPs through strong metal support interaction via electron donation from the metal to support. We identify that the support endowed with an amphoteric nature shows better performance. This strategy of making small metal–metal oxide NPs will open an avenue toward the rational development of efficient catalysts that would allow for other organic transformations under mild reaction conditions.
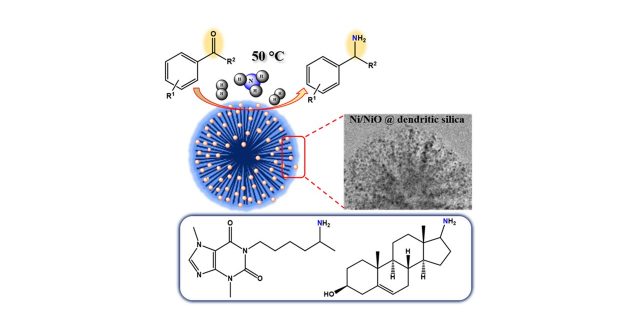
Dendritic Silica-Supported Ni/NiO Nanoparticle Catalyst enables Primary Amine Synthesis from Carbonyls at 50 °C
WRHI Newsおすすめ
Published
(Sustainable Chemical Resource Production Unit / Dr. Michikazu Hara, Dr. Debraj Chandra and Dr. Manas Bhunia)
“Synergistic Effects of Earth-Abundant Metal–Metal Oxide Enable Reductive Amination of Carbonyls at 50 °C”
ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces (DOI:10.1021/acsami.1c21157)
For details, click here.
<Abstract>
