Catalytic Activity of Atomic Gold-Decorated Polyaniline Support in Glucose Oxidation
Published
(Laboratory for Materials and Structures / Dr. Mark Chang)
“Catalytic Activity of Atomic Gold-Decorated Polyaniline Support in Glucose Oxidation”
Electrochem (DOI: 10.3390/electrochem1040026)
<Abstract>
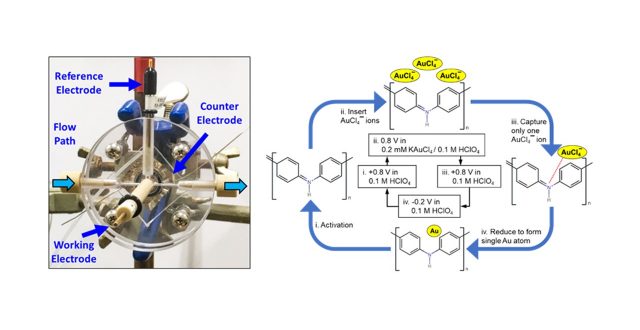
Atomic-level gold clusters are decorated on a polyaniline (PANI) support by a cyclic atomic electrodeposition process, and the catalytic activity in the oxidation of glucose is studied. The evaluation is conducted by cyclic voltammetry using atomic-level gold clusters-decorated PANI (PANI/AuN, where N indicates the atomic size of the Au cluster and N = 1~3 in this study) as the working electrode and a solution containing 0 to 50.0 mM of glucose in phosphate-buffered saline. The catalytic activity is determined from the oxidation current observed at around +0.6 V vs. Ag/AgCl. The catalytic activity is found to be affected by the size of gold clusters decorated on the PANI/AuN, whereby the catalytic activity is low when N is 1 or 3. On the other hand, an obvious enhancement in the catalytic activity is observed for the PANI/Au2 electrode.
For details, click here.
