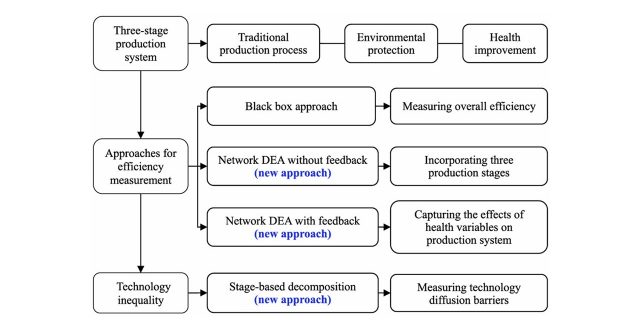
The existing studies on Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) neglect the effects of health variables on labor force participation (input) and production system. To overcome the drawback, this study formally proposes the concept of environment-health DEA and investigates how to construct it. Methodologically, our new approach, consisting of three models, overcomes the following methodological difficulties: (a) how to structure the environment-health DEA and how to identify its methodological advantages, (b) how to measure technology inequality and how to identify technology diffusion barriers originated from different stages. Empirically, this study examines Chinese provinces from 2009 to 2017. The main conclusions are as follows. First, there are significant differences between the black box approach and two network DEA approaches. Thus, a model selection matters much for our empirical analysis. Second, health variables should play an important role in determining unified efficiency and efficiency improvement potential. Finally, technology inequality rises over time across Chinese provinces and technology diffusion barriers occur in all production stages.
【Available online】New concepts for environment-health measurement by data envelopment analysis and an application in China
WRHI News
Available online
(School of Environment and Society / Dr. Toshiyuki Sueyoshi)
”New concepts for environment-health measurement by data envelopment analysis and an application in China”
Journal of Cleaner Production(DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127468)
For details, click here.
<Abstract>
