【論文】Tunable vertical ferroelectricity and domain walls by interlayer sliding in β-ZrI2
WRHIからのお知らせ おすすめ
フロンティア材料研究所 Sergey Nikolaev特任助教の国際共著論文
“Tunable vertical ferroelectricity and domain walls by interlayer sliding in β-ZrI2“
が、 npj Computational Materials に掲載されました。(DOI:
10.1038/s41524-021-00648-9
)
詳しくはこちら
<Abstract>
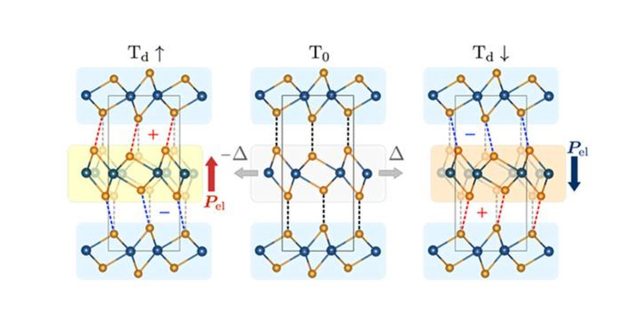
Vertical ferroelectricity where a net dipole moment appears as a result of in-plane ionic displacements has gained enormous attention following its discovery in transition metal dichalcogenides. Based on first-principles calculations, we report on the evidence of robust vertical ferroelectricity upon interlayer sliding in layered semiconducting β-ZrI2, a sister material of polar semimetals MoTe2 and WTe2. The microscopic origin of ferroelectricity in ZrI2 is attributed to asymmetric shifts of electronic charges within a trilayer, revealing a subtle interplay of rigid sliding displacements and charge redistribution down to ultrathin thicknesses. We further investigate the variety of ferroelectric domain boundaries and predict a stable charged domain wall with a quasi-two-dimensional electron gas and a high built-in electric field that can increase electron mobility and electromechanical response in multifunctional devices. Semiconducting behaviour and a small switching barrier of ZrI2 hold promise for various ferroelectric applications, and our results provide important insights for further development of slidetronics ferroelectricity.
