3D columnar silica (glass) nano-domes show anisotropy at IR wavelengths and can be used for radiative cooling and sensors
WRHIからのお知らせ おすすめ
物質理工学院 森川淳子教授とSaulius Juodkazis特任教授の国際共著論文
“Anisotropic 3D columnar micro-film coating for applications in infrared and visible spectral ranges”
が、Applied Surface Science に掲載されました。(DOI:10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.152910 )
詳しくはこちら
<Abstract>
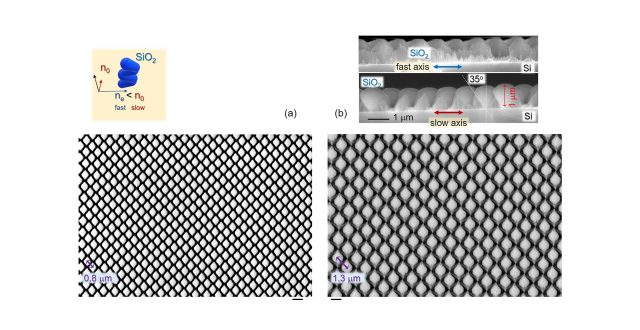
Polarisation analysis of thin (
∼1μm
) SiO
2
films deposited via evaporation at a glancing angle of 70°to the normal on resist pillar arrays was carried out using synchrotron-based Fourier transform infrared (s-FTIR) microspectroscopy in reflection mode. Changes in intensity of absorption bands were observed to follow the angular dependence of
∼cos2θ
, consistent with the absorption anisotropy. The strongest absorption was found to be the sharp Si-O-Si stretching vibrational mode at 1040
±
20 cm
−1
, which can be used for sensor applications, as well as radiative cooling in the atmospheric transparency window, within the range of 8-
13μm
(i.e. 1250-769 cm−1). Anisotropy of IR absorbance is correlated with retardance/birefringence of the same patterns in the visible spectral range. Larger period patterns of 3D columnar SiO
2
films of
∼1μm
in thickness deposited on polymer/resist pillar arrays provide the possibility to control anisotropy of the form-birefringent 3D columnar films.
