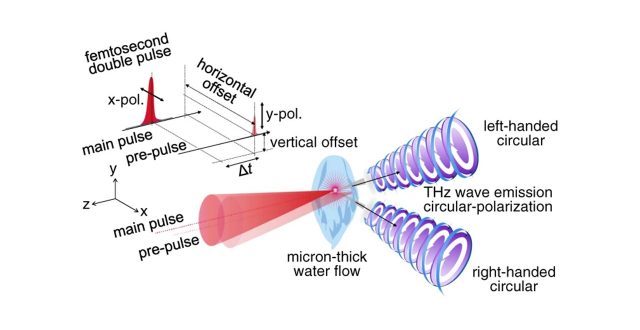
A point-like single-cycle circularly polarised THz emission is realised from focal volume of subwavelength (for THz) dimensions
WRHIからのお知らせ おすすめ
物質理工学院 Saulius Juodkazis特任教授の国際共著論文
“Spatio-temporal control of THz emission”
が、Communications Physics に掲載されました。(DOI:10.1038/s42005-022-00914-2 )
詳しくはこちら
<Abstract>
Intense THz sources are expected for further progresses in nonlinear THz science and technology. Liquids like water are durable and continuously-reusable under intense laser irradiation for THz emission though such studies on THz emission from water targets are so far limited. Polarisation fine control of THz emission is demonstrated with a tilted micro-thin water flow by the irradiation of two cross-linearly-polarised femtosecond laser pulses (800nm, 35fs, transform-limited) with spatio-temporal offsets. With an optimized horizontal offset at ∼11 μm between the ∼8 μm focal spots and time delay at 4.7ns, circularly-polarised THz emission is obtained with its intensity enhancement more than 1,500-times if compared with the single pulse irradiation. It is shown that the photon-number-based efficiency from the laser to THz at 7.1 x 10−3 is achieved with the optimisation of the double pulse irradiation. Polarisation-resolved THz time-domain spectroscopy and time-resolved shadowgraphy imaging reveal that the circularly-polarised THz emission originates from the focal volume in front of the water flow. Coupling between a shockwave due to air-breakdown and water ablation-mediated mass transport by the pre-pulse with a laser wake-field along the optical path of the main pulse is responsible for the point-like single-cycle THz emission.
