The thermal properties of novel nanomaterials play a significant role in determining the performance of the material in technological applications. Herein, direct measurement of the temperature diffusivity of nanocellulose-doped starch–polyurethane nanocomposite films was carried out by the micro-contact method. Polymer films containing up to 2 wt%. of nanocellulose were synthesised by a simple chemical process and are biodegradable. Films of a high optical transmittance
T
≈
80
%
(for a 200
μ
m thick film), which were up to 44% crystalline, were characterised. Two different modalities of temperature diffusivity based on (1) a resistance change and (2) micro-thermocouple detected voltage modulation caused by the heat wave, were used for the polymer films with cross sections of ∼100
μ
m thickness. Twice different in-plane
α
∥
and out-of-plane
α
⊥
temperature diffusivities were directly determined with high fidelity:
α
∥
=
2
.
12
×
10
−
7
m
2
/s and
α
⊥
=
1
.
13
×
10
−
7
m
2
/s. This work provides an example of a direct contact measurement of thermal properties of nanocellulose composite biodegradable polymer films. The thermal diffusivity, which is usually high in strongly interconnected networks and crystals, was investigated for the first time in this polymer nanocomposite.
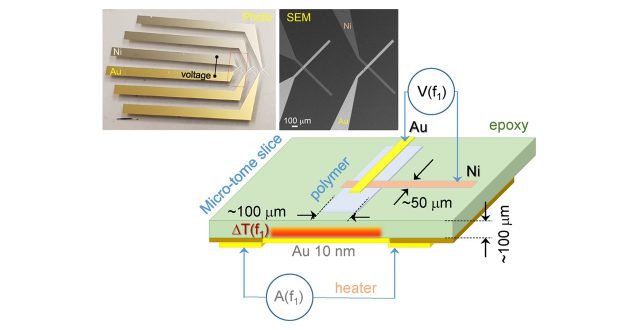
Thermal properties of a bio-degradable polymer doped with nano-cellulose were directly measured with micro-thermocouple
WRHIからのお知らせ おすすめ
物質理工学院 森川淳子教授とSaulius Juodkazis特任教授の国際共著論文
“Direct Measurement of Temperature Diffusivity of Nanocellulose-Doped Biodegradable Composite Films”
が、Micromachinesに掲載されました。(DOI: 10.3390/mi11080738 )
詳しくはこちら
<Abstract>
