-
International Collaborative Research Project on Statistical Physics Modeling of Socio-Economic Phenomena
We are focusing on modelling socio-economic phenomena through the analysis of huge amounts of precise data. Such Big Data analyses allows us to construct mathematical models using statistical physics. Using this quantitative approach, we aim in the prediction and regulation of social phenomena. The main subjects of our research are financial markets, business firm trading networks, words in cyber-space and human flow patterns using GPS.
-
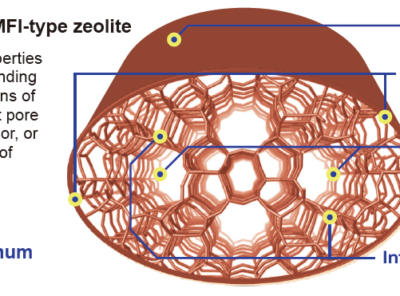
Determination of the Distribution of Al on T-Sites in MFI-type Zeolite
Zeolites are widely used as heterogeneous catalysts in industrial chemical processes because of their strong acidity and shape selectivities. The acidic properties of aluminosilicate-type zeolites originate from protons that balance the negative charge induced by framework Al atoms in tetrahedral sites (T sites). The catalytic properties of zeolites depend on various factors, including pore structure, acid strength and the amount of acid.
-
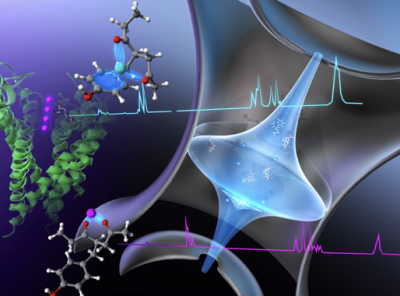
Advanced Laser Spectroscopy on Highly Functional Molecular systems
Development and analysis of highly functional molecular systems such as supramolecules and biofunctional molecules are at the frontier of chemistry and material science research. This international collaboration focuses on molecular recognition in biological systems (Fujii, Ishiuchi, Lisy, Dopfer, Zehnacker-Rentien and Xantheas), excited state hydrogen and proton transfer in large molecular systems (Fujii, Miyazaki, Ishiuchi and Jouvet) and solvent migration dynamics in molecular clusters (Fujii, Miyazaki and Dopfer). Using a combination of advanced laser spectroscopy and high-level computational chemistry, we aim to reveal the mechanisms underlying the superior functions of these molecular systems.
-
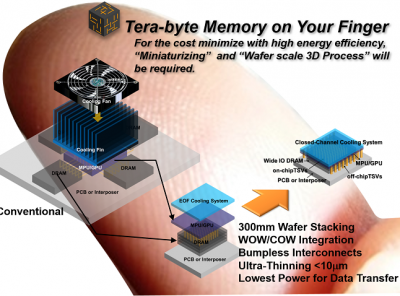
Three-Dimensional Semiconductor Process Integration/International Project for Heterogeneous and Functional Integration
In this project, we will characterize bonding materials to ensure high-reliability interconnects by evaluating the mechanical characteristics of the bonding materials in stack process and the electrical characteristics of vertical interconnects. Since circuit design (which can be thought of as the floor plan of the device) is derived from conventional planar scaling, it is possible to increase bandwidth fan-out and reduce power consumption in 3D devices through the use of high-density short interconnects without bumps in stack devices. Based on these technologies, it will become possible to manufacture ultra-small systems 1000 times smaller than current technologies comprising terabyte storage memory and microprocessor capabilities.
-

Assessment of RC shear walls under seismic loading
Slender reinforced concrete walls are an important part of a building’s lateral load resisting systems. The 1999 Standard for Structural Calculation of Reinforced Concrete Structures [2] mandated the use of structural walls with boundary columns. In 2010, the standard was revised to allow structural walls with rectangular cross sections for buildings higher than five stories. To avoid catastrophic failure, structural walls are normally designed to have high shear resistance relative to flexural resistance and consequently fail in a ductile flexural mode.
-

Japan-Germany Joint Research Platform for Development of Selective Precipitants for Nuclear Fuel Materials
Development of Simple and Versatile Nuclear Fuel Recycling Technology Based on Genuine Actinide Chemistry
Actinide ChemistryNuclear Energy SystemNuclear Fuel Recycling
-
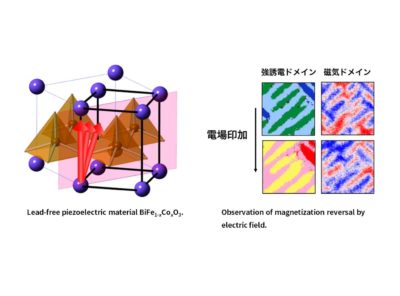
International collaborative research project for the development of environmentally friendly functional oxide materials
In order to realize an internet of things (IoT) society in which all devices are connected to the Internet, it is important to reduce the power consumption of electronics while developing materials that have a low environmental impact. We are designing novel materials through first principle calculations and conducting, precise structural analyseis of these materials using quantum beam and advanced characterization techniques,.
-
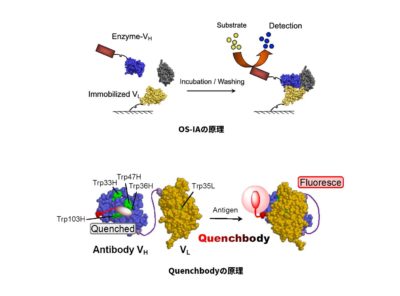
International Collaborative Research Project on Next Generation Immunosensor
In this project, we aim to develop novel antibodies against biomarker proteins, low molecular weight hormones and environmental pollutants using a range of techniques, such as phage display technology. Using the antibodies identified, we will also develop new immunosensors that are simple, fast and highly sensitive. We anticipate that this research will lead to practical applications, including clinical diagnosis and environmental pollutant detection systems.