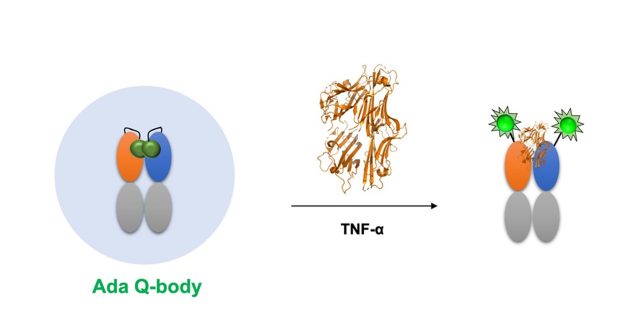
腫瘍壊死因子を簡便迅速に検出可能な蛍光免疫センサーQ-bodyの開発
WRHIからのお知らせ おすすめ
化学生命科学研究所 上田宏教授とJinhua Dong特任教授の共著学術論文
“Quench-release-based Fluorescent Immunosensor for the Rapid Detection of Tumor Necrosis Factor α”
が、ACS Omega に掲載されました。(DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.1c03941 )
詳しくはこちら
<Abstract>
Tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) is used as a biomarker for the diagnosis of various inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. In recent years, numerous approaches have been used for the qualitative and quantitative analyses of TNF-α. However, these methods have several drawbacks, such as a tedious and time-consuming process, high pH and temperature sensitivity, and increased chances of denaturation in vitro. Quenchbody (Q-body) is a fluorescence immunoprobe that functions based on the principle of photoinduced electron transfer and has been successful in detecting various substances. In this study, we constructed two Q-bodies based on a therapeutic antibody, adalimumab, to rapidly detect human TNF-α. Both sensors could detect TNF-α within 5 min. The results showed that the limit of detection (LOD) of TNF-α was as low as 0.123 ng/mL with a half-maximal effective concentration (EC50) of 25.0 ng/mL using the TAMRA-labeled Q-body, whereas the ATTO520-labeled Q-body had a LOD of 0.419 ng/mL with an EC50 of 65.6 ng/mL, suggesting that the Q-bodies could rapidly detect TNF-α with reasonable sensitivity over a wide detection range. These biosensors will be useful tools for the detection and monitoring of inflammatory biomarkers.
