副腎皮質ホルモン・アルドステロンを簡便迅速高感度に検出可能な免疫プローブの開発に成功
本態性高血圧や副腎腫瘍の早期診断への貢献に期待
WRHIからのお知らせ おすすめ
化学生命科学研究所 上田宏教授とJinhua Dong特任教授の共著学術論文
“Creation of a Quick and Sensitive Fluorescent Immunosensor for Detecting the Mineralocorticoid Steroid Hormone Aldosterone”
が、The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology にオンライン掲載されました。
(DOI: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2022.106118
)
詳しくはこちら
<Abstract>
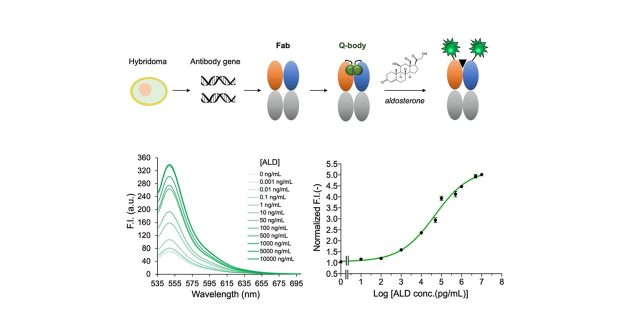
Aldosterone (ALD) is a steroid hormone secreted by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex that mainly acts on the kidney to regulate sodium ion and water reabsorption. Detection of ALD plays an important role in the diagnosis of primary aldosteronism in patients with hypertension. For the first time, the gene encoding the anti-ALD antibody, A2E11, was successfully cloned and analyzed using phage display technology. The antibody had an affinity of 2.5 nM against ALD, and after binding to ALD, it reached saturation within 5 s. Using this antibody, a Quenchbody (Q-body) was constructed by labeling the N-termini of heavy and light chains of the antigen-binding fragment of A2E11 with the fluorescent dye ATTO520 to detect ALD based on the principle of photoinduced electron transfer. The sensor detected ALD in 2 min, and the limit of detection was 24.1 pg/mL with a wide detection range from 24.1 pg/mL to 10 µg/mL and a half-maximal effective concentration of 42.3 ng/mL. At the highest concentration of ALD in the assay, the fluorescence intensity increased by 5.0-fold compared to the original fluorescence intensity of the Q-body solution. The Q-body could be applied to analyze 50% of human serum without a significant influence of the matrix. The recoveries of ALD in spiked serum samples with the Q-body assay were confirmed to range from 90.3 to 98.2%, suggesting their potential applications in the diagnosis of diseases, such as essential hypertension.
